To grow a real bonsai by all the rules, it takes 25 years and a very complex formation of small trees. Today, lovers of this culture can get homemade bonsai by growing a plant like portulacaria. The article will introduce the description of the species, the rules for the care and maintenance of the flower in room conditions.
What is portulacaria - plant description
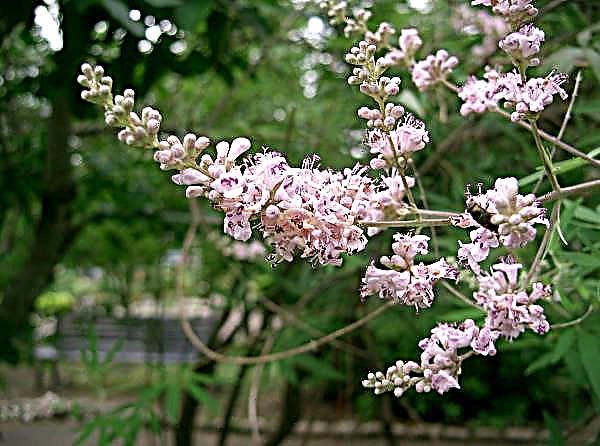
Portulacaria is a fast-growing ornamental succulent that can be used as a new culture as bonsai and ampelous. Portulacaria is not a frequent guest in home gardening and park design, but boasts ease of care and stamina.
For a long time, this plant in the botanical classification belonged to the Portulakov family, but now it is sometimes ranked among the small genus of perennial Succulents of the Didieri.
There are different opinions about whether this genus unites 5 species of endemic succulents (living in a limited area) or is of the same type and is represented by only one species - African portulacaria (Portulacaria afra), which is also called portulacaria afra, portulacaria bonsai, "elephant food" .
The native land of the natural growth of the portulacaria is the South African region - dry forests and deserts of Africa with an extremely hot and arid climate, sultry sun and excessively low humidity.
In the process of such natural selection, the plant as a result of adaptation to natural conditions acquired specific features:
- low dependence on moisture;
- the change in photosynthesis that goes along the C4 path - the leaves absorb carbon dioxide at night, and during the day they close the stomata to prevent evaporation of moisture (transpiration);
- a small number of pore-stomata in the epidermis of the leaf;
- leaf cover coating;
- a clear change of seasonal activity to a state of rest and sleep.
Did you know? Translated from Chinese, the name of the plant is "a golden braid with jade leaves." So called the daughters of the imperial family. The shape of the plant with natural growth is similar to a small head (side shoots with leaves) with a pigtail (reddish stalk).
The life form of African portulacaria is a leafy perennial succulent, bonsai, possessing such botanical characteristics:
- winding woody shrub, which in indoor conditions develops in the form of dense, compact trees;
- height in the natural environment - up to 3.5 m, in the indoor version - up to 1 m;
- the stem as it grows from brick red becomes wrinkled and dark brown;
- randomly growing thick and juicy shoots;
- opposite oval leaves can reach 5 cm, but in a room culture they are smaller, the color is light green, pink fringing and specks of light spots are possible;
- the flowers are small but numerous (2-3 mm), the color gradually changes from grassy to light pink with various shades;
- flowers are collected in inflorescences (7 cm) in the form of spikelets at the ends of the processes;
- shoots are easy to shape into silhouettes and images.
Using the ability of the plant to change the color of the leaf plate depending on the illumination, breeders bred two types of African portulacaria:
Both species lose their mottled color in low light and become almost white with pinkish shades of leaves in good light.
Optimal conditions for growing in the house
In indoor culture, desert plants lose their ability to adapt to a different habitat.
The grower needs to create growing conditions close to natural, taking into account the properties of portulacaria:
- drought tolerance;
- love of heat and the sun under direct rays;
- no shading, even slight;
- insensitivity to differences in night and day temperatures;
- the need for an active phase followed by rest.
Did you know? The Japanese word "bonsai" consists of two components: "bon" - a container and "sai" - a tree. This is the ancient art of growing small trees in small containers according to the strict rules of crown formation.
- The unpretentious portulacaria cannot stand:
- excessive waterlogging of the soil;
- sharp fluctuations in microclimatic indicators (temperature, humidity of air and soil);
- reacts by dropping leaves to adverse conditions.
Location and Lighting
When choosing a place for the normal development of the photophilous portulacaria, you need to remember that she is not so afraid of bright sunlight as shading. The best place will be the windows of the western and southern directions. The decorativeness of a flower depends on the brightness of the lighting.

In summer, you can arrange a plant walks in the fresh air in warm weather, even direct sunlight will do. In a dark room or in cloudy weather, it may be necessary to illuminate with phytolamps.
Temperature mode
Natural climatic conditions for portulakaria - high temperature and low humidity - correspond to the microclimatic indicators of our region in the summer. In winter, in a state of sleep, the flower needs to be provided with a cool place with a temperature of about + 10 ° C ... + 15 ° C. Freezing should not be allowed, which will lead to the death of portulacaria.
Air humidity
A desert resident of Pursulakaria will tolerate dry and hot air more easily than high humidity. High humidity often causes diseases and pests. The plant does not need spraying. For aesthetic purposes only, can a flower be arranged to shower to cleanse dust.
Home Care
Portulacaria can be used for growing:
- in the home collection with light windows;
- in greenhouses and botanical winter gardens;
- in office and public buildings;
- The plant is suitable for the formation of artificial bonsai.

Watering and feeding
Portulacaria is accustomed to drought and rare rainfall in the natural environment, therefore it needs only careful and rare watering, and in the phase of rest and sleep it can do without irrigation at all. Watering is carried out only with the complete drying of the earthen coma in pots about once a month. The flower is not so sensitive to the hardness of the water, but it is advisable to avoid chlorine, so the water should be settled and at room temperature.
Top dressing is carried out very rarely with complex mineral fertilizers for succulents. Such fertilizers are characterized by a low content of minerals, namely nitrogen. Fertilize fertilizers with water and combine with the next watering. In the autumn-spring dormant period, all feeding is stopped.
Pruning
Portulacaria tolerates even the strong pruning that is necessary to create a bonsai culture of conceived original shapes, sizes and images. To limit the growth of the plant, pinch or shorten young shoots. Formation is best done in the spring, and pinching - at any time of active growth. 
Professional artificial bonsai is formed using wire. For portulacaria, this method is unacceptable because of the possibility of injuries and damage to the flower.
After pruning, it is necessary to carefully select the watering regime, since the leaves on the plant become much smaller, it consumes less water. With waterlogging, water will accumulate in the soil, which can lead to decay and root damage. To create sufficient moisture during this period, the flower must be sprayed.
Transfer
The soil mixture for growing portulacaria should be light and loose in order to ensure moisture and air permeability. A suitable substrate is suitable for cacti and succulents. You can prepare the composition yourself by mixing the turf soil and coarse sand evenly. Part of the sand can be replaced with fine gravel, vermiculite, zeolite or perlite.
Slow-growing portulacaria does not need frequent transplants. Only young plants are transplanted during propagation. Adults transplant when filling with the root system the entire volume of the pot.
New transplant pots must be wide and stable to prevent capsizing. At the bottom of the tank for good drainage pour 2 cm of drainage material - expanded clay, broken brick without dust, pebbles, pieces of foam. This will eliminate stagnation of water during irrigation.
Video: Trimming and transplanting African Purslane
Flowering period
In home collections, it is practically impossible to observe the flowering of portulacaria. Such a rare occurrence can only be admired in greenhouses or in the botanical garden.
Many amateur gardeners use the need of a flower for a long and strict dormant period for subsequent flowering and try to force the plant to bloom, creating extreme conditions for it: do not water it at all, keep it in darkness and cold during dormancy.
That is, to imitate the situation when the plant faces real death, and thereby activating its self-protective properties in order to survive and bloom in the active phase. But so far there are no results of such a method.
Methods of reproduction at home
Portulacaria breeding is possible with:
- seed;
- cuttings;
- layering.
Seed propagation is a rather rare type of breeding. If you managed to get or buy seeds, then they should be sown in a slightly moist soil and covered with a film, monitoring moisture and airing the crops as needed.
In spring and summer, propagation by cuttings can be carried out. To do this, thick stems with four opposite leaves (at least 15 cm) are separated by an oblique cut. The slice is dried for several days, the lower leaves are removed, and then the stalk is planted in a slightly moistened substrate. The rooting process lasts about three weeks. When young shoots reach a height of 20-30 cm, you can pinch off the tops on several internodes to stimulate branching.
Important! As cuttings, you can use pruned branches during the decorative formation of bonsai.
When propagating by layering, an adult branch is enough to bend to the ground and secure with a wooden stud. After a while, the branch will take root. A new shoot can be separated and transplanted into a new container.

Possible growing difficulties
Portulacaria is practically not affected by diseases and pests - it is a fairly resistant plant to diseases. But in case of violation of the requirements for care, when the plant is weakened or infected from neighboring plants, the appearance of powdery mildew is possible, and from pests - scabies, mealybug, spider mite.
To eliminate it, it is necessary to use chemicals for indoor plants according to the instructions (Apollo, Di-68, Chemidis, Rogor S), which will help in the fight against the pest. It is advisable to alternate the means to avoid addiction, treat the planting material with colloidal sulfur. With a strong infection, treatment with a systemic insecticide will also be required.
Important! In free growth, portulacaria can reach 1 m. To limit the growth of room culture of portulacaria bonsai, it is necessary to constrain the root system with a small pot or trim a third of the entire root mass.
Closely monitoring the development of the plant and the state of the soil, you can notice the signs of diseases or lack of care in time:
- drops leaves - the conditions of detention are violated, namely the temperature is increased - in winter it is necessary not higher than + 15 ° C; improper lighting (window direction, room corner);
- after pruning, the leaves fall off - reduce watering, allow the soil to dry, but it is necessary to spray the plant;
- leaves darkened, twigs drooped - possibly frozen. Trim the entire blackened part, sprinkle the place of cut with charcoal or cinnamon;
- shoots are stretched and do not form branches - lack of light or excess moisture in the soil;
- rot roots - remove the plant from the pot, wrap the roots with paper, which change as they get wet, in this way dry the roots from excess moisture, leave the plant to dry for several days;
- the leaves wrinkle, dry out and subsequently fall off - the natural aging process, the wrong regime and the amount of watering (excess or deficiency).
The green plant collection has become an integral part of residential and office space. And landscape design provides for the presence of trimmed bushes and trees. Artificial bonsai created with the help of the African portulacaria will be an original and attractive addition.