The apple-tree Korobovka is less and less found in old horticulture, and is also used in breeding work. Features of the variety and the basics of agricultural technology are described below.
Grade history
Korobovka is an old folk variety, the first scientific mention of which, according to some sources, dates back to 1855. Its name is associated with characteristic small fruits, which are often sold on the market in boxes. It can be found under the names Skorospelka or Medunichka. Features of the variety led to its exclusion from zoning, however, the plant grows in many household plots. Korobovka takes part in the breeding of new varieties, is included in the collection of the Biological Reserve (Warsaw, Poland) and the Estonian list of ancient apple trees.
Features of the variety led to its exclusion from zoning, however, the plant grows in many household plots. Korobovka takes part in the breeding of new varieties, is included in the collection of the Biological Reserve (Warsaw, Poland) and the Estonian list of ancient apple trees.
Description and characteristic
The box is positioned as a summer apple tree, whose fruits are ready for harvest in late July or early August (depending on the region of cultivation).
Did you know? In Germany, there was an old custom to plant an apple tree on the child's birthday. At the same time, the growth and development of the tree was a prediction of the fate of man.
Tree
Trees of this variety are described as medium-sized, they are characterized by such signs:
- height 4–5 m;
- sprawling and wide crown;
- shoots of dark brown color with dense leathery leaves;
- fruiting at the ends of branches, sometimes on fruit twigs.
Boxing requires additional pollinators, the best of which are Cinnamon Striped, White Pouring and Papirovka. Flowering occurs in medium terms. The tree is not early and begins to bear fruit from about the 7th year of life, which is offset by a long fruiting period (up to 50 years).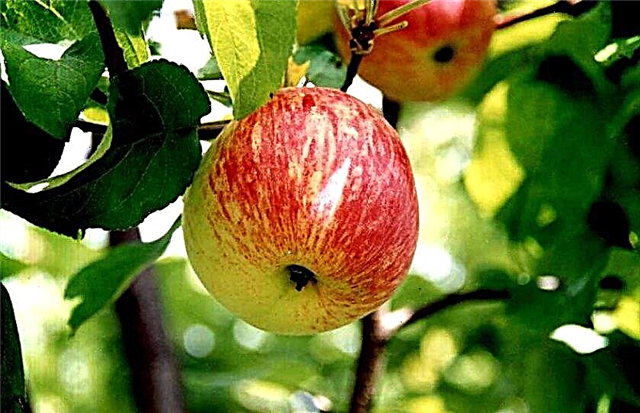 The maximum yield is 60–70 kg per tree, but, having reached its 20th anniversary, Korobovka switches to periodic productivity, while the fruits become even smaller. The variety is valued for its high winter hardiness and drought tolerance, as well as low soil composition. The box has an average resistance to scab and is often affected by the codling moth.
The maximum yield is 60–70 kg per tree, but, having reached its 20th anniversary, Korobovka switches to periodic productivity, while the fruits become even smaller. The variety is valued for its high winter hardiness and drought tolerance, as well as low soil composition. The box has an average resistance to scab and is often affected by the codling moth.
Fruit
Small apples of this variety have the following features:
- weight 30-50 g;
- flattened, smooth shape;
- the skin is thin and dense;
- color is yellow or greenish with orange-red short stripes;
- the flesh is yellowish, dense and juicy;
- the taste is sweet, honey, acid free.
 Boxing apples are popular for their exceptionally sweet taste. The sugar content in the fruits reaches 10%, while the acid in them contains only 0.7%. The purpose is universal.
Boxing apples are popular for their exceptionally sweet taste. The sugar content in the fruits reaches 10%, while the acid in them contains only 0.7%. The purpose is universal.Advantages and disadvantages
- The advantages of the variety are:
- high winter hardiness;
- early ripening;
- good transportability.
- The following drawbacks of Korobovka led to its exclusion from zoning:
- very small fruits;
- late onset of fruiting;
- low productivity.
Planting and subsequent tree care
A properly planted tree, which is properly taken care of, will demonstrate all the hallmarks of the variety and bring delicious fruits in the summer.
Check out such summer varieties of apple trees as:
Favorable planting dates and growing conditions
For planting a fruit tree, you can choose spring or autumn. In the case of Korobovka, which has high frost resistance, it is better to choose an autumn landing. Before the onset of cold weather, the apple tree will have time to take root and begin to develop in the spring without delay. In order for the tree to take root, at least 2-3 weeks must remain before stable frosts. For the apple tree, a sunny area with a low level of groundwater is needed. Preparation for planting an apple tree. For apple trees with a root root system, on a strong-growing stock, the water should be no higher than 3 m, and dwarf rootstocks with a horizontal distribution of roots can grow at a distance of 1.5 m from the water. The box is unpretentious to the soil composition, however acid soil should be pre-invested. For this, chalk or dolomite flour, lime is added to the soil.
Preparation for planting an apple tree. For apple trees with a root root system, on a strong-growing stock, the water should be no higher than 3 m, and dwarf rootstocks with a horizontal distribution of roots can grow at a distance of 1.5 m from the water. The box is unpretentious to the soil composition, however acid soil should be pre-invested. For this, chalk or dolomite flour, lime is added to the soil.
Did you know? Heraldry science considers the apple a symbol of peace. It is depicted on many coats of arms, and the symbols of the power of the monarch — a scepter (representing war) and an apple-shaped orb (as a sign of peace).
How to choose a quality planting material?
Exact compliance with the variety can only be obtained by purchasing in a well-known nursery or garden center. Choosing a seedling in the market, you can buy another variety. When considering the proposed range, you should pay particular attention to the stock used.
The following circumstances are taken into account:
- a tree on a seed rootstock will live for more than 50 years, while vegetative rootstocks of medium growth bear fruit for 30–40 years, and dwarf trees for no more than 20 years;
- the height of the tree on the seed stock will be the maximum possible for the variety;
- vegetative stocks bear fruit earlier;
- the previously described effect of the sensitivity of the root system to the level of groundwater;
- seed stock is more unpretentious and frost-resistant, and also demonstrates greater productivity;
- vegetative stocks allow you to place more trees on the site due to their compactness.
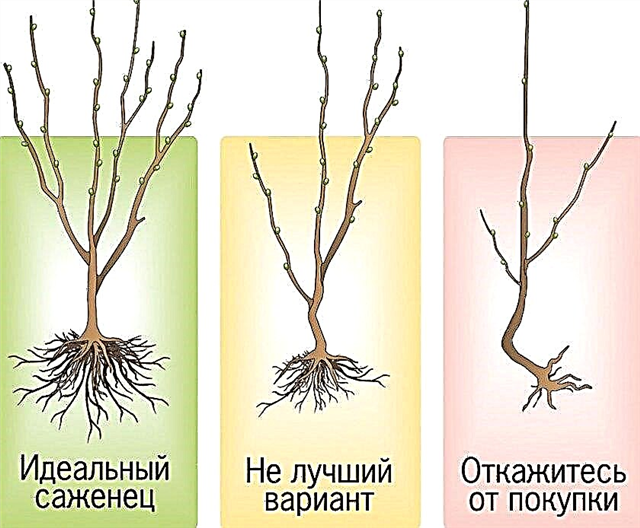
A particular seedling should have the following attributes of healthy planting material:
- a noticeable and bark-tightened inoculation site;
- bark and branches without cracks and damage by diseases;
- developed root system.
Important! When planting in autumn, only those seedlings that have already dropped the leaves should be taken. Such a plant will put all its strength into the work of the root system and take root faster.
Landing technology
In the selected area, you need to dig a hole under the volume of the roots of a particular seedling (about 70 cm deep). It is better to start preparing the pit a month before planting, in this case, freshly excavated soil will settle, and the added top dressing will enter the decomposition stage.
The excavated earth should be fertilized with the following composition:
- 1-2 cups of superphosphate;
- 2-3 full buckets of humus or peat;
- 4–5 Art. tablespoons of potassium sulfate and 8-10 tbsp. tablespoons of wood ash.
 For each tree you will need a supporting wooden peg. For an apple tree on a seed stock, temporary support is needed, so you can make a stake from linden or walnut. After a few years, such wood will rot in the ground, and the upper part can be removed.
For each tree you will need a supporting wooden peg. For an apple tree on a seed stock, temporary support is needed, so you can make a stake from linden or walnut. After a few years, such wood will rot in the ground, and the upper part can be removed.For long-term support of dwarf apple trees, a 2-meter stake of oak, with a diameter of 5 mm or more, is used. Before planting, inspect the roots and remove dry or broken elements. For additional hydration, it is recommended to put the seedling in water at night.
The algorithm for planting an apple tree is as follows:
- The selected stake is dug into the center of the pit and a fertilized earthen mixture is poured around it with a cone.
- The seedling is set on the north side of the peg and spread its roots on the surface of the cone.
- The pit is gradually covered with earth, slightly shaking the seedling and compacting the soil. The root neck (not the place of vaccination!) Should be left 5–10 cm above the soil level, and if a hole was dug the day before, it should be 10–15 cm higher.
- Then the seedling is abundantly watered (about 3 buckets of water) and, if the earth settles in the pit, add an additional layer of soil.
- The tree is tied to a peg, and the surface of the trunk circle is mulched with peat or other organics.
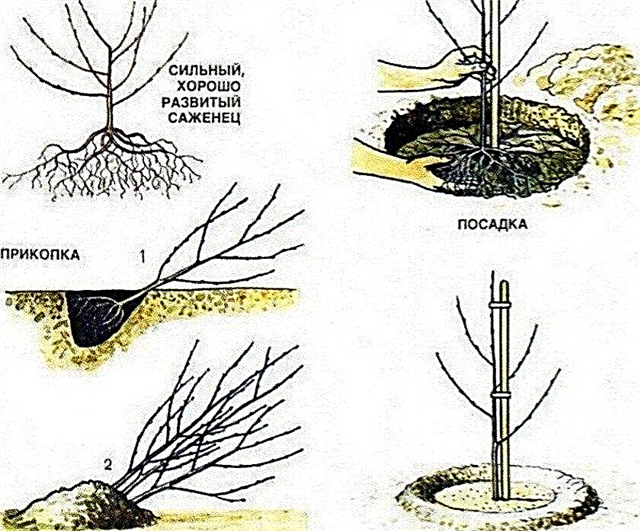 Proper planting of apple trees: 1 - laying a seedling in a trench; 2 - a seedling dug for the winter.
Proper planting of apple trees: 1 - laying a seedling in a trench; 2 - a seedling dug for the winter.How and what to water and feed the tree?
The box is drought-resistant, however, the flow of moisture should be monitored during such vegetation periods:
- in the phase of kidney swelling;
- 20 days after flowering;
- 4 weeks before harvesting;
- during foliage discharge.
For an adult tree, the number of buckets of water corresponds to the number of years of vegetation. Young seedlings should receive water more often, especially when planting on sandy soils. Every month a tree should receive at least 3-4 buckets of water, and in a dry summer it is better to water it every week. Fertilizing is an important part of gardening.
Important! Moisture-absorbing roots are located in the apple tree along the entire diameter of the crown, so watering is performed in the same way, and not just under the trunk.
Until the seedling begins to bear fruit, he will need such top dressing:
- in early spring, the root system is fed with urea, diluting 2 tbsp. tablespoons in 10 liters of water;
- the second time the tree is fertilized at the end of May by a non-root method using an Ideal or Sodium Humate solution (1 tbsp.spoon per bucket of water);
- in early autumn they spill the apple tree with a solution of superphosphate (2 tbsp.spoons per bucket of water).

A fruiting apple tree requires a different tactic and amount of fertilizer:
- in April, 500 g of urea is scattered under a tree;
- prepare a mixture of 20 l of water, 50 g of urea, 80 g of potassium sulfate and 100 g of superphosphate and leave it for a week. Before flowering, a tree is shed with infusion;
- when the flowering is completed, they feed the apple tree with a solution of nitrophoska and "sodium humate" (100 g and 2 g, respectively, per 20 l of water);
- when the crop is already harvested, it is necessary to introduce a bucket of humus into the soil, as well as 300 g of potassium sulfate and superphosphate. Fertilizers are dug into a groove dug along the edge of the trunk circle for half a shovel.
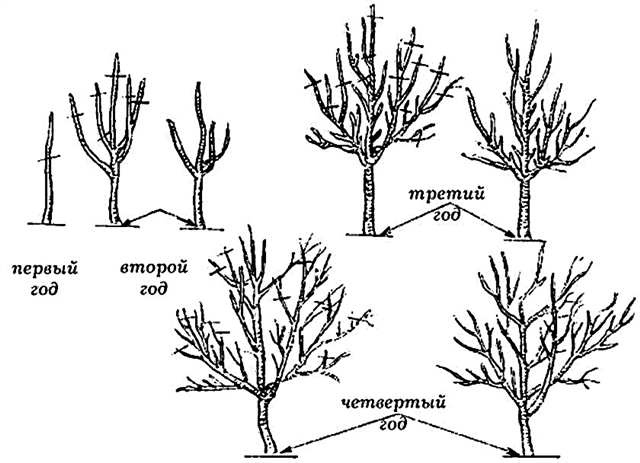
Stages of crown formation
Pruning an apple tree is performed when the tree is at rest. Korobovka refers to winter-hardy varieties, so pruning can be done in the fall. The spring procedure, however, allows the tree to recover faster due to further sunny weather and sufficient nutrition. A seedling planted in the fall begins to form in the spring, and an apple tree planted in the spring is cut off immediately.
The basic principles of crown formation are as follows:
- Annual tree more often it has only one trunk, which is cut off at a height of about 1 m. If there are side branches, they should be shortened to 40 cm, and the central conductor should be cut to 60–80 cm.
- In the second year appoint skeletal branches. For this, 3-5 shoots of horizontal direction are suitable (the angle of attachment of the branch to the trunk is not sharp, approaching a straight line). Then, all branches are shortened so that the upper branches are approximately 30 cm shorter than the lower ones, and the central trunk is 4 kidneys longer than all branches.
- On the 3rd and 4th year continue crown formation, shortening the central conductor and removing competitor branches, vertical tops, intersecting shoots and root shoots.
Fighting Diseases and Insects
The following simple techniques are good prevention of the onset and spread of diseases, and also reduce the number of pests on the apple tree:
- regular collection of carrion and destruction of mummified and decayed fruits left on branches;
- Autumn digging of the trunk circle:
- cleaning the bark, followed by disinfection and whitewashing;
- regular sanitary pruning;
- cleaning fallen leaves and plant debris.
Protective measures also include spring and autumn wood treatment with special preparations and the use of additional measures.
In the spring, work begins immediately after the snow melts and the apple tree is processed according to this scheme:
- After trimming, the trunk and branches should be sprayed with Bordeaux fluid or a mixture of urea and vitriol (copper or iron).
- When the kidneys swell, use spraying with insecticides and fungicides ("Aktara", "Biotlin", "Chorus"). During this period, traps are installed, for example, in the form of glue belts on trunks.
- As soon as the pink buds appear, you can treat the tree with the preparations “Skor”, “Karate”, “Rayek” or biological (“Fitoverm”).
- For small ovaries ("with a pea") perform complex spraying with "Fitolavin", "Aliot".
 During the ripening period, it is advisable not to use chemicals, and when using them, check according to the instructions the necessary interval before harvesting. After autumn leaf fall, they are treated with Skor, Zubr, Karbofos or Bordeaux mixture, vitriol or urea.
During the ripening period, it is advisable not to use chemicals, and when using them, check according to the instructions the necessary interval before harvesting. After autumn leaf fall, they are treated with Skor, Zubr, Karbofos or Bordeaux mixture, vitriol or urea.Important! It is recommended to alternate the preparations used in the fall every year to avoid the addictive effect.
Spraying reduces the risk of developing scab, rot, powdery mildew and other diseases. Korobovka has an average sensitivity to scab, but improper care can lead to its rapid occurrence.
Features of scab and other, most dangerous, diseases of the culture are as follows:
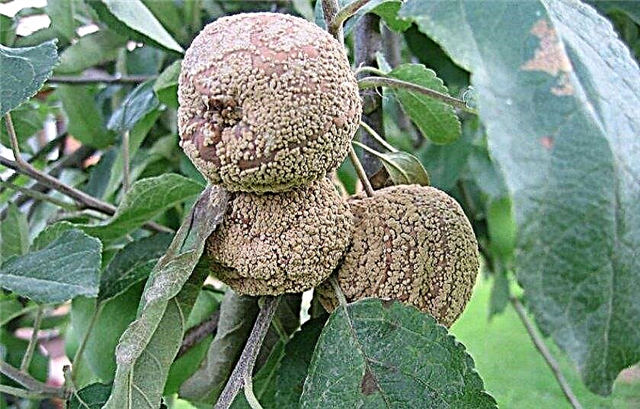
- Upon occurrence scabs Both the leaves and the fruits of the plant will be affected. The disease begins when the buds open and appear oily spots on the leaves, which then form on the fruits, covering them with a brown coating. The drug "Skor" and others containing copper and sulfur will affect this fungus.
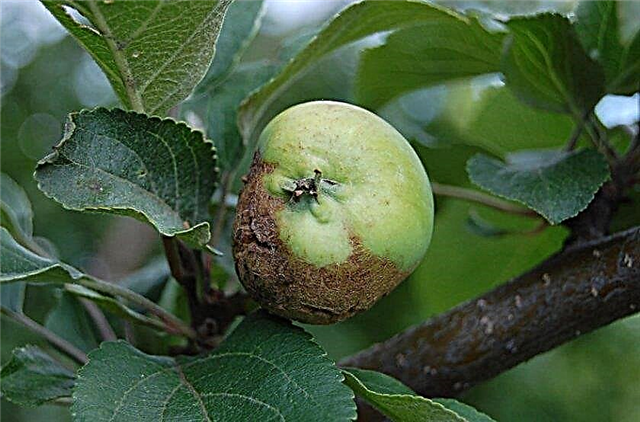

- Fruit rot more common on fruits and is already noticeable at the beginning of ripening. A small brown spot grows on the whole apple and softens it, after which the fruit falls. Copper preparations will help with this disease, but regular cleaning of diseased fruits is also important.

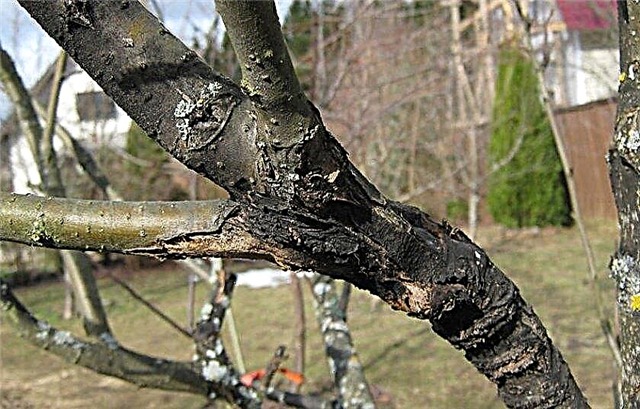
- Apple trees can hurt doggy style, often black and European. The first affects almost all parts of the plant, and the second - trunks and forks of skeletal branches. Cancer causes indented violet-brown spots on the bark, which then spread throughout the tree. Developing, the fungus leads to the death of the bark and opens the blackened wood. Fungicides used from scab affect this disease. A thorough disinfection of any wounds on the tree is also necessary.

The most dangerous pests of apple trees are such insects:
- Butterfly Codling Moth. Larvae gnaw fruit to the middle, and then crawl out and can move to the neighboring fruit. Pupae of the insect winter in the bark and soil, therefore, autumn and spring processing of the tree is extremely important.
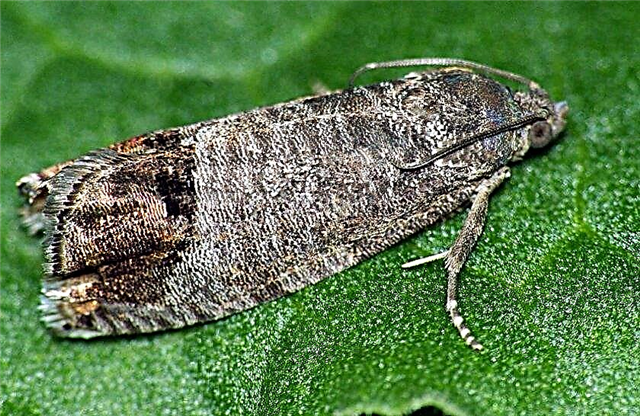

- Butterfly moth. It also harms apple trees, but its caterpillars feed on leaves and ovaries. In addition to treatments, sticky belts are quite effective for catching butterflies.
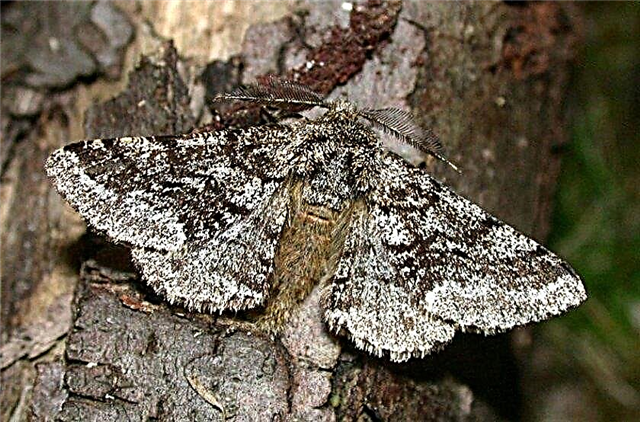

- Apple Moth. Butterflies appear in June, and their caterpillars in the spring eat young foliage. To scare away butterflies, tomatoes are planted in aisles, and damaged leaves and cocoons are collected.
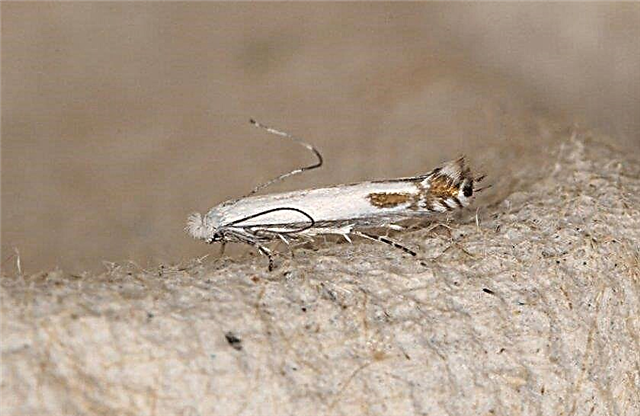

- Apple Blossom - a type of weevil, whose larvae gnaw stamens and pistils even before the flower opens. In addition to spraying, effectively simply shaking off the bugs on the film under the tree.
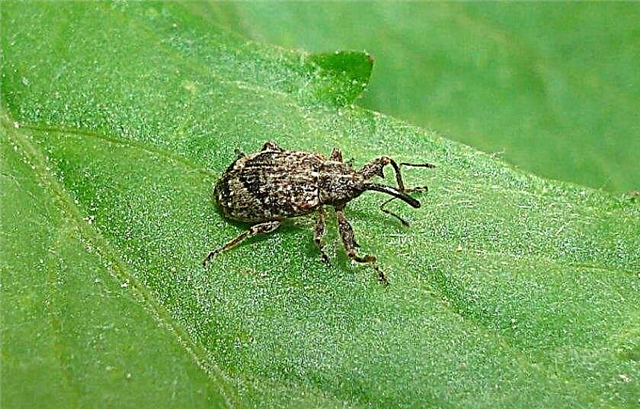

Preparing a tree for winter
To ensure an easy wintering for the apple tree, timely water-loading irrigation and fertilizing will help, as well as the following operations:
- whitewashing with protective compounds will prevent the formation of frost pits during thaw periods. Pre-clean and disinfect the bark;
- harvesting carrion and fallen leaves, followed by digging and additional mulching (before the onset of frost);
- young seedlings should be wrapped with spruce branches or roofing paper, roofing felt or other material.
Harvesting and storage
The fruits of the Box are held tightly on branches and only damaged apples are showered. After harvesting, it is recommended to immediately use the fruit for its intended purpose, since during storage (up to 1 month) their taste is significantly impaired. Korobovka continues to attract gardeners with the honeyed taste of fruits and winter hardiness, and also gives life to new varieties with improved characteristics.