Existing varieties of watermelons allow you to get a crop for the summer period, even in the middle zone of the RF. Now a lot of unpretentious hybrids with excellent taste are bred. Let's get acquainted with the medium early variety of watermelon Bedouin F1, its characteristics and features, advantages and disadvantages, the rules of cultivation and storage.
Origin of the variety
The Bedouin F1 watermelon variety belongs to the Dutch hybrids. It was brought out by breeders of the Bejo Zaden company (Netherlands). This is one of the leading firms for the selection and production of vegetable seeds. Its developments are aimed at obtaining varieties resistant to diseases and adverse factors, which have excellent taste and high yield. The Bedouin F1 watermelon hybrid is unpretentious and has proven itself under different growing conditions.
Description and description Bedouin F1
The Bedouin F1 watermelon has a mid-early ripening period, approximately on the 80th day from the appearance of seedlings. It has great growth power and forms powerful lashes. Each plant matures from 1 to 3 fruits. This variety allows some thickening of plantings without loss of performance. It is permissible to plant up to 7 thousand plants per 1 ha. Fruits grow oval and with an average weight of 8-10 kg. Their surface is covered with a spectacular “tiger” color with alternating light green and dark green stripes with an uneven edge.
Did you know? There are about 1200 varieties of watermelons. The following 4 categories are distinguished from the whole variety: with seeds, without seeds, small watermelons, yellow watermelons.
The peel thickness is average (13 mm). In ripened watermelons of this variety, the sugar content of the pulp can reach 13%. It is crispy, juicy and red, with a few seeds. Fruits have good keeping quality. These watermelons are consumed fresh and suitable for processing. The variety is resistant to Fusarium infection, develops normally and gains good sugar content under adverse conditions. It can be grown in open and closed ground.
Features of growing in different regions
In the southern regions, Bedouin F1 watermelon seeds can be sown immediately in the ground when the earth warms up to + 15 ... + 16 ° С. In the conditions of central Russia, it would be wiser to use the seedling method or film shelters. In the Urals and Siberia, these watermelons can be grown in greenhouses made of polycarbonate or coated with a double layer of transparent film. In greenhouses, this culture is tied up on trellises.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- The following advantages of the Bedouin F1 watermelon are noteworthy:
- excellent taste;
- good transportability;
- resistance to diseases and adverse conditions;
- good adaptive abilities;
- excellent accumulation of sugar;
- presentation of the fruit;
- the possibility of thickening landings.
- The disadvantages are very conditional:
- the cost of seed is higher than that of local varieties;
- the impossibility of collecting and using their own seed material from the hybrid;
- not the earliest harvesting dates.
Did you know? Watermelon consists of 90% of water, so it well saturates the body with water in the heat. Moreover, the presence of calcium, magnesium, sodium and potassium in the striped berry allows you to keep moisture at the required level.
Growing Features
Both the use of the seedling method and the sowing of Bedouin F1 watermelon seeds in the ground have their own nuances.
How to plant seedlings
Before planting seedlings, you should prepare a place for it and plan it correctly in order to buy the right amount of plants.
Preparing beds and choosing a place to plant
The place for planting watermelons is chosen in the southern, well-lit place. The site must also be reliably protected from the wind. Groundwater should not come close to ground level. The beds themselves form a height of about 15 cm with a slope to the south.
This plant crop prefers light sandy or sandy soils with a neutral reaction. For planting, choose a place where perennial grasses, cabbage, winter wheat, onions, and legumes grew earlier. Bad predecessors are considered to be pumpkin plants (watermelons, zucchini, melons, cucumbers), as well as tomatoes, peppers, potatoes, and eggplant.
Important! On the site where the watermelons grew, re-planting the same culture is possible only after 6 years.
To prepare the soil for planting melons in the autumn during digging, organic and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are added. It is also good to add wood ash or dolomite flour. For 1 m² it is recommended to add 40 g of superphosphate, 30 g of ammonium sulfate, 4–5 kg of rotted manure and 20 g of potassium salt.
Disembarkation technology
Seedlings are planted, usually in the period from late May to early June. Grown or acquired seedlings are planted on the bed according to the following pattern: between rows 1,5–2 m, and between plants - 0,7–1 m. Planting up to 70 plants per hundred is allowed. Watermelon planting pattern: 1 - Planting density-7888 pcs / ha; 2 - Planting density-7930 pcs / ha. Seedlings are instilled up to cotyledon leaves. After planting, the soil should be slightly tamped, and around the planted plants - sprinkled with sand to prevent rot. Then the seedlings must be watered. For this purpose, warm water is used.
Watermelon planting pattern: 1 - Planting density-7888 pcs / ha; 2 - Planting density-7930 pcs / ha. Seedlings are instilled up to cotyledon leaves. After planting, the soil should be slightly tamped, and around the planted plants - sprinkled with sand to prevent rot. Then the seedlings must be watered. For this purpose, warm water is used.
Sowing scheme immediately in open ground
Watermelons are planted in open ground in seeds only in the southern regions with a fairly warm climate. The soil should warm up to + 15 ° C. Before sowing seed material must be processed. You can conduct heat treatment: place them in a thermos with water heated to + 50 ° C. After the sprouts hatch, the seeds need to be removed. For sowing, 8 cm deep wells are prepared with a gap of 1 m between them.
If in the fall no fertilizer was applied to the site, then 1 teaspoon of ammofoski, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of ash and 1 kg of humus. Then 2 liters of water should be poured into such a hole, and then, at an equal interval from each other, place 2-3 seeds. Then fill the hole with soil and tamp a little. Re-watering is not necessary. After 1 week or later, the first shoots should appear. After the formation of 3-4 true leaves, it is necessary to thin out, leaving the strongest specimens.
Watermelon Care
To get the maximum yield of watermelons, it is necessary to organize the right care for them, which consists in watering, fertilizing, forming a bush, as well as combating ailments.
Watering
Bedouin F1 watermelons must be watered. The first time, hydration is carried out approximately 1 time per week at the rate of 30–35 liters per 1 m². Watering is largely dependent on weather conditions. In the heat should be watered more often - 2 times a week. It is important to provide plants with enough water during the appearance of color.
Over the entire period, this crop must be abundantly watered 3-4 times:
- during the appearance of 6-7 leaves;
- during flowering;
- during the formation of the fruit.
 2 weeks before harvesting, moisturizing is stopped so that the watermelons acquire the necessary sugar content. After the watermelon bushes grow, weeds will no longer be able to harm their development, so they can not be pulled out after a while. Loosening should also be stopped so as not to injure the roots.
2 weeks before harvesting, moisturizing is stopped so that the watermelons acquire the necessary sugar content. After the watermelon bushes grow, weeds will no longer be able to harm their development, so they can not be pulled out after a while. Loosening should also be stopped so as not to injure the roots.Top dressing
14 days after transplanting seedlings into the soil, they begin to feed it. When fertilizing for the first time, ammonium nitrate is used based on a ratio of 20 g per 10 liter bucket of water. For 1 bush goes 2 liters of such a solution. You can also use slurry from chicken droppings in a proportion of 1:20 or manure (1:10). In such a solution, organics are mixed with 15 g of calcium chloride and 30 g of superphosphate. The second feed is carried out at the beginning of the appearance of color. For 1 plant use 6 g of superphosphate and 4 g of ammonium nitrate and calcium chloride.
Important! If you apply fertilizers in the dry form for feeding watermelons, you need to water the plants before and after making nutrients.
Bush formation
To obtain a good harvest of these juicy berries, it is necessary to make a bush. For this purpose, extra shoots should be removed. This procedure is carried out when the fruit grows the size of a chicken egg. For the formation, choose sunny weather so that the sections of the sections dry quickly. 3 fruits are left on the stem, and pinch lateral shoots above the 4th leaf so that they do not grow. Scheme of the formation of a bush of watermelon. Short shoots provide the flow of nutrients to the main stem. As the watermelons grow, a corresponding removal of the lateral processes and stepsons is carried out, starting with those that are closer to the root system. As the berries grow, different plywood and small boards should be placed under them to avoid rotting.
Scheme of the formation of a bush of watermelon. Short shoots provide the flow of nutrients to the main stem. As the watermelons grow, a corresponding removal of the lateral processes and stepsons is carried out, starting with those that are closer to the root system. As the berries grow, different plywood and small boards should be placed under them to avoid rotting.
Pest and Disease Control
Unfortunately, this plant crop can be affected by various diseases, as well as some pests. Therefore, to obtain a crop, it is important to identify the problem in a timely manner and take measures to eliminate it. It is imperative that agricultural cultivation techniques be observed, since weak plants are ill and exposed to pests, especially weak plants.
Did you know? A watermelon of record weight, listed in the Guinness Book of Records, was grown by American Chris Kent in 2013. This fruit had a mass of 159 kg.
The main diseases of watermelons:
- Powdery mildew. This disease of fungal origin manifests itself in the form of a light gray coating on the leaves, which gradually begin to die. The fruits become deformed and lose their taste, and then rot.
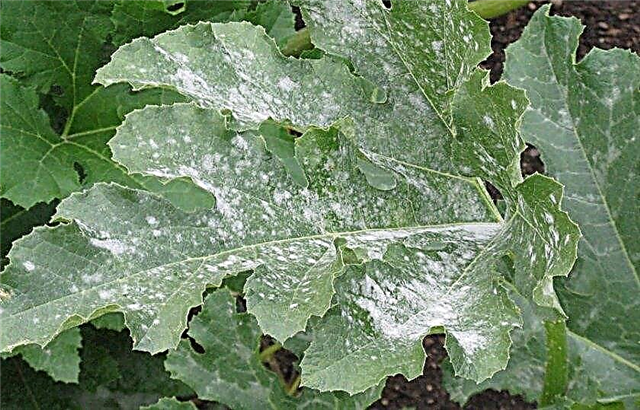

- Peronosporosis. Initially, it affects the old leaves, and eventually - young ones. A violet-gray coating forms on the back of the leaves. Berries begin to deform and slow down their growth.
- Olive spotting. Signs of the presence of the disease are spots throughout the plant. The leaves begin to deform, and on the shoots and petioles, olive formations appear. The ovary dries and falls.

- Angular spotting (bacteriosis). On leaves affected by this disease, oily whitish spots form, in the place of which holes appear. The leaves die off, the shoots dry, and the fruits stop growing and begin to rot.
- Anthracnose. This fungal disease can be seen on the yellow-brown spots with pinkish-yellow pads on the leaves. In addition, when a high humidity is established, a pinkish coating appears. Over time, the bush dries.

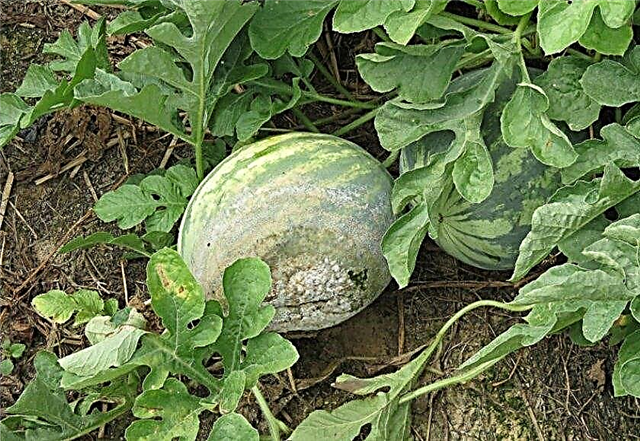
- Rot. It happens gray, white, black and brown. It affects shoots, leaves and fruits. And brown rot also destroys the roots of the plant.

- Cucumber mosaic. This viral disease is not treatable. It appears as a pattern on the leaves in the form of a mosaic, which has a green color. The bush slows down its growth and development, and tubercles and dots form on its surface.
Watermelons can also be affected by such pests:
- Wireworm. These are the larvae of nutcracker beetles, they are similar to pieces of wire. The pest infects seeds and sprouts.
- Gourd aphids. It feeds on the juice of a plant and tolerates various diseases.
- Winter scoops. The larvae (caterpillars) of this insect feed on the plant and gnaw at its roots. The bush turns yellow and dies.
 To combat diseases of fungal origin, chemical preparations such as Bordeaux fluid, the preparations Decis, Fundazol, and Skor are used. To avoid the occurrence of diseases, you must follow the rules of crop rotation, disinfect the seeds, and arrange proper care for the plants. Some pests and diseases can be eliminated using folk methods.
To combat diseases of fungal origin, chemical preparations such as Bordeaux fluid, the preparations Decis, Fundazol, and Skor are used. To avoid the occurrence of diseases, you must follow the rules of crop rotation, disinfect the seeds, and arrange proper care for the plants. Some pests and diseases can be eliminated using folk methods.For example, tobacco dust and ash are good for aphids. These ingredients are mixed in a 1: 1 ratio and plants are sprinkled on. Then you need to spray the landing water. After 20-30 minutes, the soil must be loosened, which will contribute to the destruction of insects that have fallen on the soil. To get rid of pests, bait and traps are also used.
Harvesting and storage
Watermelons should be removed at the initial stage of maturity. If you collect unripened fruits, then they may not reach the necessary maturity in the storage place. But overripe watermelons are not suitable for long-term storage. Bedouin F1 watermelon varieties do not lose their taste and marketability for about 40–45 days after collection. Watermelons are harvested as they mature. The fruits are suitable for pickles, pickling. However, it is best to use them fresh. For longer storage, medium-sized specimens are taken and without mechanical damage. Then they are placed in a well-ventilated dark room. The optimum temperature should be at the level of + 2 ... + 5 °, and humidity - about 80%. You can also briefly store the fruits in the apartment.
However, it is best to use them fresh. For longer storage, medium-sized specimens are taken and without mechanical damage. Then they are placed in a well-ventilated dark room. The optimum temperature should be at the level of + 2 ... + 5 °, and humidity - about 80%. You can also briefly store the fruits in the apartment.
Important! Watermelons should not be torn, but cut off with lashes. For collection use a well-sharpened knife or pruner.
To do this, choose a cool and dark place, and the berries themselves must be turned over daily. Bedouin F1 watermelon can be grown in different regions of Russia, using the seedling method and shelters in the middle lane, and greenhouses in the more northern regions. In addition, planting a watermelon of this variety can be compacted to later collect large crops of striped berries.