Monstera is a popular plant that can often be found in homes and office premises. Large carved leaves of saturated color look great in any interior. In order for the plant to please the eye, it is necessary to adhere to the basic rules of care, which will be discussed in this article.
Plant description
Monstera is a representative of the tropics. Her homeland is South and Central America. The most common monstera is lovely (another variant of the name is delicious). This evergreen vine with leaves up to 45 cm long can reach a height of several meters. The main features of the monstera are:
The main features of the monstera are:
- long thick stalk;
- leathery leaves with slits along the veins along the entire length of the sheet;
- cob shaped inflorescence;
- fruits are berries.
Did you know? The name comes from Latin monstrum (which means "monster") and is quite consistent with the size of an adult plant.
Indoor cultivation conditions
Monstera is known for its unpretentiousness, but there are several conditions that must be strictly observed. One of the conditions is the temperature regime:
- in summer, the optimum temperature is +22 - + 25 ° C;
- during the winter months, +16 - + 18 ° C will be sufficient.
 Monstera feels good in a shaded place, but a deep shadow should be avoided so that the leaves do not become small and pale. In the event of direct sunlight, the plant must be protected. Adult plants react sharply to changes in light conditions, so it is undesirable to rearrange the tub.
Monstera feels good in a shaded place, but a deep shadow should be avoided so that the leaves do not become small and pale. In the event of direct sunlight, the plant must be protected. Adult plants react sharply to changes in light conditions, so it is undesirable to rearrange the tub.Humidity in the room is very important for the monstera, because its native habitat is humid tropics. If there is a lack of moisture, drying out is possible, and too much moisture will cause droplets of water to appear on the floor. It is also recommended to wipe the leaves more often and spray them with warm, settled water.
Important! The juice of the plant is toxic and irritates the skin, as well as the mucous membranes.
Methods of reproduction at home
Monstera propagates quite easily - by cuttings, but there are certain nuances in each of the ways. They start breeding in the spring. For rooting, you can use different parts of the plant. A section of the stem is disinfected with a powder of charcoal, which must be finely ground.
Apical cuttings
 The tops of adult plants are taken, cut off and placed in a vessel with water. It will take some time for the roots to appear.
The tops of adult plants are taken, cut off and placed in a vessel with water. It will take some time for the roots to appear.
Before planting a plant in a pot, you must wait at least three shoots.
Even more roots contribute to better rooting of the cuttings.
Stem cuttings
 It will take a thick part of the stem with 2 or more buds. This will be the stalk. It is placed on prepared soil (or hydrogel) so that the kidney touches the soil surface.
It will take a thick part of the stem with 2 or more buds. This will be the stalk. It is placed on prepared soil (or hydrogel) so that the kidney touches the soil surface.
Then the stalk is covered with a film or glass (a kind of greenhouse will turn out), periodically watered and sprayed.
From time to time, a clear protection is removed for ventilation. The stalk is transplanted to a permanent place after the roots appear.
Leaves
This is not the easiest and most reliable way, but it can be used if there are no other parts of the plant. The cut off (or broken off) leaf is put in a jar of water and wait for the roots to appear.
Did you know? The first leaves of the monstera have a heart shape, and carved leaves appear a little later.
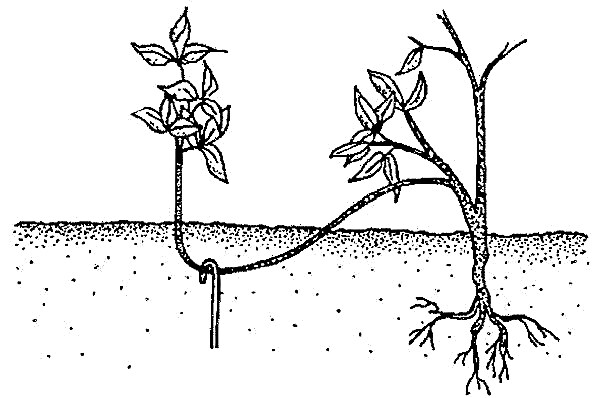
Layering

Air layers require a lot of effort, but they take root much better than the leaves or tops. It is necessary to find an escape with strong aerial roots and give them extra moisture.
You can tie the moss and constantly moisten it with water or attach a small plastic bowl with water.
You should also protect the roots from drying out with a film by loosely wrapping it around a part of the plant. After the appearance of a sufficient number of roots, the layers are separated and transplanted into the pot.
Seeds
Seeds are rarely used to propagate a monstera. They germinate after 2–4 weeks in a warm and well-lit place. Adult carved leaves appear at 5–8 months. Seedlings need a dive, then they need to be planted, and then transplanted annually. A developed root system is formed in them after 2 years. After rooting, the plant lives in an intermediate small pot, and the monster is transplanted into a volumetric tub in 3-4 years.
Important! Liana monstera needs support, which can be a stick or grille, as well as stretched cords.
Further care
The roots of the plant, which provide the vital activity of the monstera, require special attention. They must be lowered into the ground of the main pot or, having collected in a bundle, placed in an additional container with earth. Monstera aerial roots can cling to the wall.
Watering and fertilizer
To water, remember that soft water is suitable after settling. Abundant watering is maintained from March to August, and from autumn it is reduced to moderate in the winter months. From the moment of drying of the top layer several days are counted (usually 2-3) and only then watered. Adult monster is fed once every 2 weeks from April to August. Both mineral and organic fertilizers are used for complex type deciduous plants, alternating them. The dosage indicated in the instructions is reduced by 2 times. Young plants do not need fertilizer.
Adult monster is fed once every 2 weeks from April to August. Both mineral and organic fertilizers are used for complex type deciduous plants, alternating them. The dosage indicated in the instructions is reduced by 2 times. Young plants do not need fertilizer.
Transfer
Recommended Reading

Liana grows very quickly and requires transplants at first every year, then from 4 years every 2 years. After 5-6 years, the plant grows so much that the transplant becomes unnecessary. Topsoil is replaced every year. The transplant is carried out in the spring.
For planting monstera use a mixture consisting of:
- 3 parts of turf;
- 1 part of peat, sand, earth and humus.
At the bottom, it is necessary to lay a quality drainage.
Pruning
Regular pruning is not necessary for the monstera. The top is trimmed for branching and growth of the side shoots. In this case, the support will need to be strengthened and a sprawling liana should be provided with a spacious place.
The period of rest and flowering
Flowering periods in indoor conditions are extremely rare, sometimes it is possible only in the greenhouse or conservatory. In good conditions, the flower may appear in the second year of life. Cob fruits when ripening turn purple. They are edible, reminiscent of pineapple in taste. The rest period in tropical plants, to which monstera belongs, does not stand out. They are looked after the same throughout the year.
Growing difficulties
Florists when breeding monstera can face several problems. The most common difficulties are:
- yellowing and softness of the leaves. These are symptoms of excessive watering, and their lack will be manifested in the appearance of brown dry spots on the sheets;
- the sheet changes color to transparency. Chlorosis is possible, from which iron chelate will help get rid (use according to the instructions);
- problems with leaves. That “fault” is incorrect lighting;
- leaves without slits. It is a lack of nutrition;
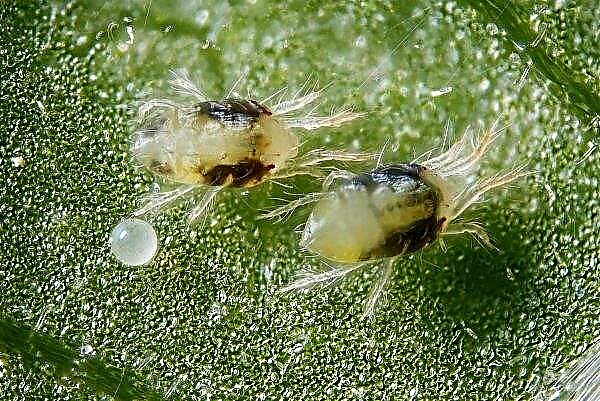
- attack of parasites and pests (for example, scabies or spider mites). You can get rid of them with the help of special drugs.
Care and reproduction of monstera is within the power of each grower. However, it is necessary to really assess the conditions under which it is planned to grow the plant. Liana requires a large space and is not suitable for a small room.